3.0 - Systems and components
Learn about technical data and technical explanations about electric motors, drive trains, battery packs and energy use. Videos, diagrams and articles explain specific elements and specific parts of electrical vehicles.
Chapters
1.0 - About batteries
Nissan Leaf batteries: How an Electric Car Battery is Made
2.0 - About Fuel Cell
3.0 - About Flywheel
Different explanations about how Flywheel works
4.0 - Ultracapacitors
Different explanations about ultracapacitors
5.0 - Induction motors
How does an Induction Motor work ? and a Model S, Tesla Motors.
6.0 - Synchronous Motor
How does an Synchronous Motor work ? and a Model Audi Q5 hybrid quattro
7.0 - SRM Motor
8.0 - Power Converters
Toyota's New Silicon Carbide Power Semiconductor
9.0 - Test your Knowledge
Systems and components
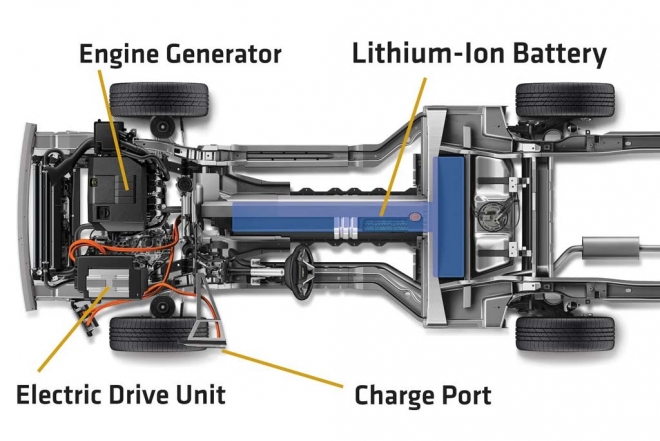
Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) use an electric motor for traction, and chemical batteries, fuel cells, ultracapacitors, and/or flywheels for their corresponding energy sources.
The electric vehicle has many advantages over the conventional internal combustion engine vehicle (ICEV), such as:
- an absence of emissions
- high efficiency
- independence from petroleum
- and quiet and smooth operation
The operational and fundamental principles in EVs and ICEVs are similar, as described in Module 2. There are, however, some differences between ICEVs and EVs, such as the use of gasoline tanks vs. batteries, ICE vs. electric motor, and different transmission requirements. This module will focus on the methodology of power train design and will investigate the key components including traction motor, energy storages and power converter.
Conclusions
ESS HV BATTERIES.
All manufactures of EV base mounted Lithium Ion, an element that is found in very specific points of planetary geographical. This reality clearly hampers the production of these technologies on a larger scale and greatly affects its price and production volume. Toyota base mounted NI-Metal in HEV vehicles.
The Lithium-ion battery provides energy density of about 150-170 Wh/kg and between 170 and 200 Wh/kg (in the case of Tesla).
Durability of deep complete cycles of 3000 (full charging and discharging).
Load times range from 30 minutes (quick charge) at 10 h in the slow mode (conventional plug)
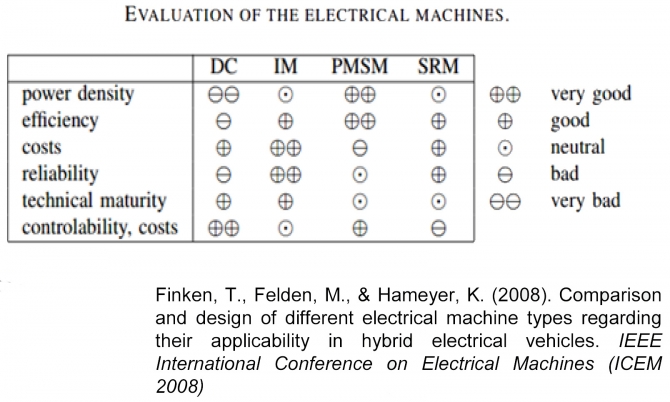
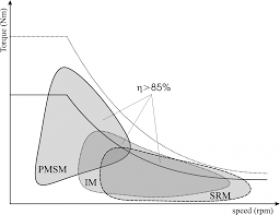
XX. EMOTOR COMPARATIVE. Technology Resume.